DATABASE-AS-A-SERVICE
Database-As-A-Service with private cloud
Large enterprises today have hundreds and thousands of databases of various versions, configurations and patch levels. Another challenge is around time to provision new databases. When an end user, be it a developer or a QA engineer, needs a database he or she typically has to go through an approval process, which then translates into a series of tasks for the DBA, the sysadmin and storage admin. This is a cumbersome and time-consuming process and may span days. Due to non-optimal usage of finite computational resources and significant IT latency, it also possesses the risk of overspending by organizations.
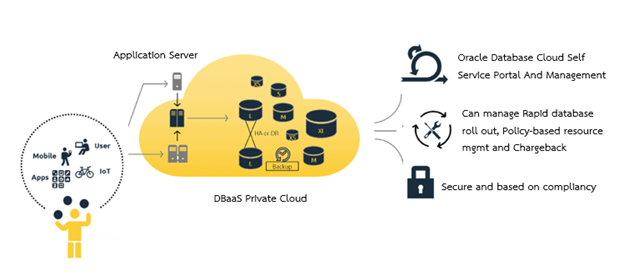
Cloud (private, public and hybrid) and Database as a Service (DBaaS) are two interlocking concepts that IT managers are considering to modernize, automate and transform their data centers. DBaaS can help IT teams modernize their database infrastructure and address their business drivers as follows:
- Virtualization
Virtualization can increase IT agility, flexibility, and scalability while creating significant cost savings. Workloads are deployed faster, performance and availability increases, and operations become automated, resulting in IT that’s simpler to manage and less costly to own and operate. Virtualization also makes better use of available resources. - Standardization
One of the biggest challenges is dealing with database sprawl with different versions and configuration of databases. This makes managing and administrating a database very difficult and time consuming. By implementing DBaaS, administrators can standardize how databases are built for each version and ensure that best practices are followed, making administrating the databases easier and less time consuming. - Automation
Being able to implement automation within DBaaS removes the manual processes, which are time consuming and prone to user errors. Automation increases the stability of database environments and improves compliance and governance. Automation reinforces the implementation of standards, enhancing agility and time-to-market. - Self ServiceLifecycle Management
DBaaS creates a self-service catalog for users to provision and deactivate a database. The catalog helps enforce governance and approval workflows for each database and maintains the lifecycle of a database. - Monitoring and Metering
As part of any DBaaS implementation, being able to monitor and meter each database is very important. Monitoring an Oracle database is done through Oracle Enterprise Manager, which simplifies the administration of each database and the overall database environment. Metering allows IT organizations to measure and charge groups based on usage, thus enabling better management of databases and control over license costs.
Component Product Solution:
- Oracle Exadata or Oracle Database Appliance
- Oracle Database Enterprise Edition
- Oracle Database Options
- Oracle Multitenant
- Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC)
- Oracle Partitioning
- Oracle Database In-Memory
- Oracle Diagnostics Pack
- Oracle Tuning Pack
- Oracle Database Lifecycle Management Pack for Oracle Database
- Oracle Advanced Security
- Oracle Database Vault
- Oracle enterprise manager cloud management pack
